Orthopedic Surgery
Orthopedic Surgery

Orthopedic Surgery
Orthopedic surgery serves as a cornerstone in the comprehensive management of sports injuries and age-related musculoskeletal conditions, offering patients a pathway towards recovery, restoration, and rejuvenation. By leveraging innovative surgical techniques, evidence-based practices, and multidisciplinary approaches, orthopedic surgeons empower individuals to overcome physical limitations, pursue active lifestyles, and embrace the joys of movement and vitality across diverse age groups and athletic endeavors. As advancements in orthopedic science continue to evolve, the promise of improved outcomes and enhanced patient experiences underscores the enduring significance of orthopedic surgery in promoting musculoskeletal health, mobility and well-being.
What is Sports Injuries Orthopedic Surgery
Sports injuries are a common occurrence among athletes of all levels, ranging from amateur enthusiasts to professional competitors. These injuries encompass a spectrum of musculoskeletal trauma, including ligament tears, tendon ruptures, cartilage damage, and fractures, often resulting from sudden impacts, overuse, or improper techniques during physical activities. Orthopedic surgeons play a pivotal role in diagnosing and treating sports-related injuries, employing a combination of surgical and non-surgical treatments tailored to the specific needs of each patient.
One of the most prevalent sports injuries is anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) rupture, frequently encountered in athletes participating in sports that involve pivoting and sudden changes in direction, such as soccer, basketball, and football. Orthopedic surgeons utilize advanced techniques such as arthroscopic ACL reconstruction to restore knee stability and function, enabling athletes to return to their pre-injury levels of activity with reduced risk of re-injury.
Moreover, orthopedic surgery addresses other common sports injuries like rotator cuff tears, meniscal tears, and stress fractures through procedures such as rotator cuff repair, meniscal repair or resection, and bone grafting, facilitating optimal recovery and rehabilitation for athletes striving to resume their athletic pursuits.

Orthopedic Surgery at a Glance
What is Age Related Orthopedic Surgery
As individuals age, the musculoskeletal system undergoes physiological changes characterized by the gradual degeneration of bones, joints, muscles, and connective tissues, predisposing older adults to orthopedic conditions such as osteoarthritis, osteoporosis, spinal stenosis, and degenerative disc disease. These age-related ailments often manifest as chronic pain, stiffness, diminished mobility, and functional impairment, significantly impacting the overall quality of life.
Orthopedic surgery emerges as a vital therapeutic option for elderly patients grappling with debilitating musculoskeletal disorders, offering surgical interventions such as joint replacement (e.g., total hip arthroplasty, total knee arthroplasty), spinal fusion, and osteotomy to alleviate pain, restore mobility, and enhance physical function.
Total joint replacement surgeries, in particular, have revolutionized the management of severe osteoarthritis and joint degeneration in older adults, providing durable prosthetic implants that mimic the natural anatomy of the affected joints, thereby relieving pain and enhancing joint function, enabling patients to enjoy a more active and fulfilling lifestyle in their later years.
Cosmetic & Plastic Surgery


Dr. Burak Pasinlioğlu
Aesthetic & Plastic Surgery
Frequently Asked Questions
Arm lift surgery, also known as brachioplasty, aims to reshape the upper arms by removing excess skin and fat, resulting in a more toned and contoured appearance.
Ideal candidates for arm lift surgery typically have excess skin and fat on the upper arms, often due to factors such as weight loss or aging, and desire improvement in arm contour and appearance.
During arm lift surgery, incisions are made along the inner arms to remove excess skin and fat. The underlying tissues are then tightened, and the remaining skin is repositioned for a smoother, firmer appearance.
The recovery process after arm lift surgery involves temporary swelling, bruising, and discomfort, which can be managed with prescribed pain medication. Patients are advised to limit arm movement and avoid strenuous activities during the initial healing phase.
Like any surgical procedure, arm lift surgery carries some risks, including infection, bleeding, scarring, and changes in sensation. However, these risks can be minimized by choosing a skilled and experienced plastic surgeon and following post-operative care instructions diligently.
Arm lift surgery involves making incisions along the inner arms, which may result in visible scars. However, a skilled plastic surgeon will take care to place the incisions in discreet locations and minimize their visibility. Over time, scars tend to fade and become less noticeable, especially with proper scar care.
Yes, arm lift surgery can be combined with other cosmetic procedures, such as liposuction or body contouring surgery, to achieve comprehensive body rejuvenation. However, the decision to undergo multiple procedures should be carefully discussed with your plastic surgeon to ensure safety and optimal results.
JCI CERTIFICATION
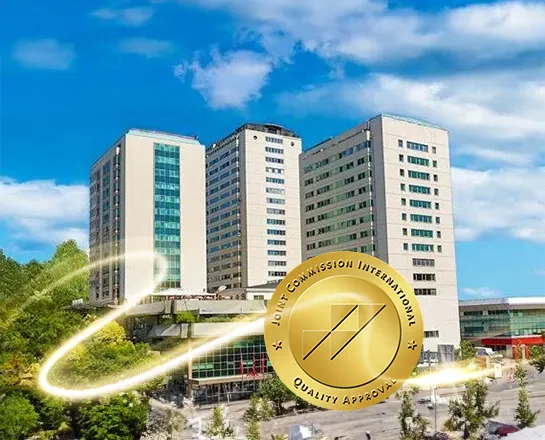

In line with the importance we attach to quality and reliability in healthcare services, our clinically contracted hospitals are certified by JCI (Joint Commission International) to comply with international standards. JCI certification plays a key role in guaranteeing the quality and reliability of the healthcare services we provide to our patients. Under contract with TrustMed, the hospital, located in Şişli, is a point where healthcare excellence, advanced technology and strategic accessibility meet. This medical facility is a testament to advanced technology and infrastructure, with a team of nationally and internationally recognised specialists offering warm and personalised services to its patients.
Regular audits are critical to ensure that our hospitals consistently deliver high quality services. In this way, we strive to best meet the healthcare needs of our patients and provide a safe healthcare environment.
Explore the operation further
Who can benefit from orthopedic surgery
Orthopedic surgery can benefit a wide range of individuals who experience musculoskeletal issues that impact their mobility, functionality, and quality of life. Groups of people who can benefit from orthopedic surgery:
Athletes and sports enthusiasts who sustain sports-related injuries such as ligament tears (e.g., ACL tears), meniscal tears, rotator cuff injuries, and stress fractures often require orthopedic surgery to restore joint stability, repair damaged tissues, and facilitate a safe return to sports activities.
Older adults commonly experience age-related musculoskeletal conditions like osteoarthritis, spinal stenosis, degenerative disc disease, and osteoporosis. Orthopedic surgery, including joint replacement procedures (e.g., total knee arthroplasty, total hip arthroplasty) and spinal surgeries, can alleviate pain, improve mobility, and enhance overall function, enabling seniors to maintain independence and an active lifestyle.
Individuals who have suffered traumatic injuries resulting from accidents, falls, or workplace incidents often cause significant musculoskeletal damage, including fractures, dislocations, and soft tissue injuries.
Individuals born with congenital musculoskeletal abnormalities or developmental disorders may require orthopedic surgery to correct deformities, address limb length discrepancies, and improve overall musculoskeletal alignment and function.
People with chronic musculoskeletal conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, avascular necrosis, and chronic tendonitis can cause persistent pain, inflammation, and joint dysfunction.
Patients seeking joint preservation techniques to delay or prevent the progression of degenerative joint diseases. Procedures like osteotomy, cartilage restoration, and ligament repair aim to maintain joint function and postpone the need for more extensive interventions, such as joint replacement surgery.
The ideal candidate for orthopedic surgery
The candidate should have a clearly identified musculoskeletal condition or injury that has been diagnosed through imaging studies, physical examinations, and other diagnostic tests. The condition should be one that can potentially be improved or corrected through surgical intervention.
The candidate should be in generally good health and free from significant medical conditions that could increase the risks associated with surgery and anesthesia. Conditions such as uncontrolled diabetes, heart disease, or active infections may need to be stabilized or managed before surgery can be safely performed.
It's important for candidates to have realistic expectations about the outcomes of orthopedic surgery. They should understand the potential risks, benefits, and limitations of the procedure, as well as the rehabilitation process and expected recovery time.
They should be willing and able to actively participate in the rehabilitation process as directed by their healthcare team.
They should be psychologically prepared for surgery and have the necessary support systems in place to help them cope with the physical and emotional challenges associated with the surgical process and recovery.
They should be willing and able to follow preoperative instructions provided by their healthcare team, which may include lifestyle modifications, cessation of certain medications, and preparation for the surgery and recovery period.
Ultimately, the decision to undergo orthopedic surgery should be made in collaboration with an orthopedic surgeon after a thorough evaluation of the individual's medical history, condition, and treatment goals. It's important for candidates to fully understand the risks and benefits of surgery and to weigh these factors carefully before proceeding.
Types of surgery we offer (in order of popularity)
Arthroscopic Surgery: This minimally invasive procedure involves using a small camera called an arthroscope to visualize and treat problems inside a joint. Arthroscopic surgery is commonly performed for conditions such as torn ligaments (e.g., ACL tears), torn cartilage (e.g., meniscus tears), and joint inflammation (e.g., synovitis).
Joint Replacement Surgery: Also known as arthroplasty, joint replacement surgery involves removing damaged or diseased joint surfaces and replacing them with artificial implants made of metal, plastic, or ceramic materials. Hip replacement, knee replacement, and shoulder replacement are among the most common types of joint replacement surgeries.
Fracture Repair: Orthopedic surgeons perform surgical procedures to repair broken bones and stabilize fractures using various techniques such as open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF), external fixation, and intramedullary nailing. The goal is to restore the normal alignment and function of the bone.
Spinal Surgery: Spinal surgery encompasses a variety of procedures aimed at treating conditions affecting the spine, such as herniated discs, spinal stenosis, degenerative disc disease, spinal deformities (e.g., scoliosis), and spinal tumors. Surgical interventions may include discectomy, laminectomy, spinal fusion, and vertebral column resection, among others.
Soft Tissue Repair: Orthopedic surgeons repair damaged soft tissues such as tendons, ligaments, and muscles using surgical techniques like tendon repair, ligament reconstruction, and muscle reattachment. These procedures are often performed to treat sports injuries, repetitive stress injuries, and trauma-related injuries.
Osteotomy: Osteotomy involves surgically cutting and reshaping bones to correct deformities, improve alignment, and alleviate pain in conditions such as osteoarthritis, malunions, and nonunions.
Tumor Resection and Reconstruction: Orthopedic surgeons specialize in the removal of benign and malignant tumors affecting bones and soft tissues. Surgical techniques may involve tumor resection, limb salvage procedures, and reconstructive surgeries using bone grafts or prosthetic implants.
Cartilage Restoration: Procedures such as microfracture, autologous chondrocyte implantation (ACI), and osteochondral autograft transplantation (OAT) are performed to repair damaged cartilage in joints and promote cartilage regeneration.
Our Surgeons can use surgical and nonsurgical approaches to treat musculoskeletal issues, such as sports injuries, joint pain, and back problems. Due to the type of international patients we have our surgeons would be offering surgical treatments to patients who are tired of waiting for surgical intervention in their home country or simply can’t afford the fees being charged even after their personal health insurance has covered part of the costs.
We work with top surgeons in their fields and patients need to understand that surgery is only part of the process, in many cases rehabilitation and physiotherapy will be required post-op, it will be down to the patient to decide if they will stay in Turkey for this physiotherapy or return home and our team will liaise with the patient’s doctors at home to advise on the physio required on their return.